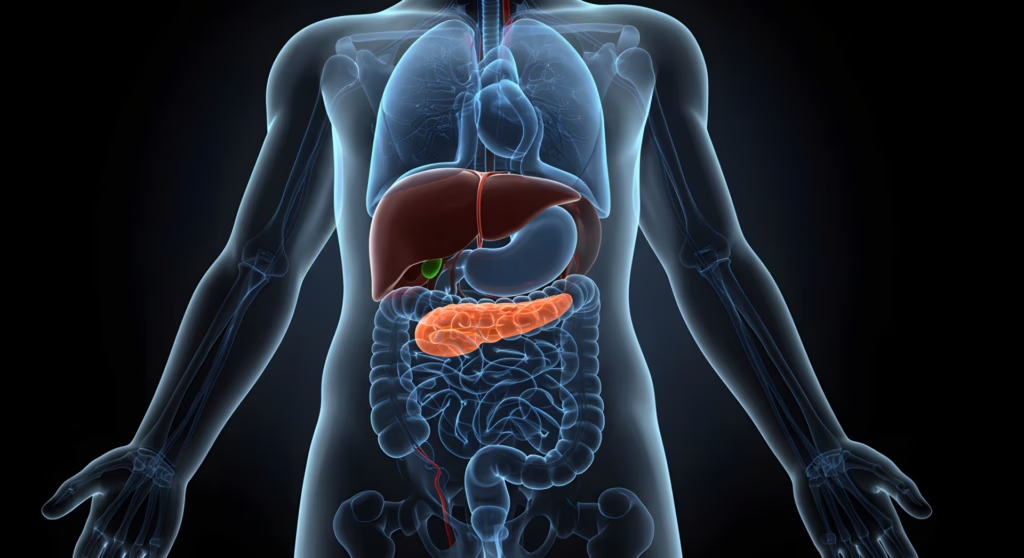
Q. What are the major challenges of treating pediatric type 1 and 2 diabetes?
Achieving optimal glycemic control in children and adolescents with diabetes remains a major challenge. Management of diabetes requires an age-specific approach, taking into account the needs and characteristics related to specific developmental stages. Variable eating patterns and physical activity, along with the limited ability to communicate symptoms of hypoglycemia/hyperglycemia are the main challenges in very young children. During adolescence, changes in insulin sensitivity related to physical growth and pubertal hormonal changes, psychological and behavioral issues and poor compliance can complicate diabetes management. Additional factors contributing to challenges in young people with diabetes include family dynamics, health status and care outside home, such as in the school setting.
Q. What have been the most important advances in the treatment of type 1 diabetes in children?
Insulin is the cornerstone of treatment of type 1 diabetes. Since its discovery almost a century ago, there have been key milestones which have improved treatment: the introduction of insulin analogues with better pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic profiles; the implementation of newer devices for insulin administrations; and alternative ways of insulin delivery. Of particular note are the recent advances in diabetes technology, these include insulin pump therapy, continuous glucose monitoring and sensor-augmented insulin pump therapy, which are leading the way towards the development of a ‘closed-loop system’ or ‘artificial pancreas’.
Developments in diabetes technology are fast-moving and hold promise to improve quality of life and outcomes. However, technology does not necessarily ‘fit’ every patient, and in children and adolescents its introduction in daily routine care can pose some psychological and ‘time-effort’ burdens, which need to be addressed.
Q. How do you treat type 2 diabetes in children who cannot meet their glycemic targets using metformin and lifestyle intervention?
Based on current recommendations, lifestyle interventions represent the first-line of managing pediatric type 2 diabetes. Metformin can be introduced if there is no benefit of lifestyle interventions.
Unfortunately, compared to adult-onset type 2 diabetes, there are fewer treatment options for youth. Up to now, metformin and insulin are the only agents approved for the management of type 2 diabetes in adolescents. Therefore, when glycemic targets are not reached, insulin is the only additional approved therapeutic option. A long-acting insulin can be firstly introduced and, if this is not enough, the addition of a meal-time short-acting insulin is the next step.
Q. Is there any evidence to support the use of other antidiabetic drugs, such as dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, or sodium-glucose cotransporter 2, in patients aged under 18 years?
Whereas many antidiabetic drugs are licensed for use in adults with type 2 diabetes in the US and Europe, only metformin is approved for pediatric use in most countries. Many clinical trials of anti-hyperglycemic agents are underway in youth-onset type 2 diabetes (NCT03429543, NCT01554618, NCT03170518) should be available in a few years.
Q. Of the above drugs, which would you expect to be most useful in a pediatric population?
There is a strong need for future studies assessing each of the above drugs in pediatric type 2 diabetes, due to potential differences in safety and efficacy profiles between different age groups. In adults, drugs such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SLGT2) inhibitors have been associated not only with reductions in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), but with other beneficial effects on weight loss, blood pressure, renal function and cardiovascular outcomes. Given that type 2 diabetes often presents a more aggressive course in the pediatric population with high rates of complications already at the time of diagnosis, SLGT2 inhibitors might be a useful therapeutic option in this age group.