Malignancies of the thyroid are one of the most common neoplasms and predominantly affect females. Differentiated thyroid carcinomas include papillary and follicular carcinomas (accounting for 90–95% of all cases).1 Papillary carcinoma is the most common type of all thyroid malignancies, while medullary thyroid carcinoma comprises 6% of all cases.1 Rarer types include anaplastic carcinomas, lymphomas and sarcomas.2 Among these, sarcomas are an extremely rare groups of tumours.1 The sarcoma types observed in the thyroid glands are liposarcoma, leiomyosarcoma (LMS), and angiosarcoma. Primary LMS of the thyroid is a rare tumour and approximately only 30 cases have been reported previously.3–22 The other common sites for LMS are gastrointestinal tract, retroperitoneum and pelvis.23
According to the histological tumour classification by World Health Organization (WHO), thyroid LMS is classified as a member of the smooth-muscle tumours of thyroid gland.24 An accurate diagnosis requires combined clinical, imaging, histological and immunohistochemistry evaluations.15 The prognosis is generally poor in spite of aggressive surgery, adjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and recurrence/relapse rates are very high with an estimated 1-year survival of only 5–10%.20 We herein report a case of 50-year-old female with primary LMS of thyroid with aggressive presentation.
Case presentation
A 50-year-old female presented to us with a 3-week history of rapidly progressive neck swelling associated with mild neck discomfort. She did not complain of any respiratory difficulty, voice change, haemoptysis, dysphagia, weight loss, loss of appetite or fever. She had no previous history of radiation exposure, no significant medical illness or surgery, and no family history of thyroid malignancy. Her physical examination revealed a large hard nodule on right side of thyroid with relative fixity to surrounding structures along with palpable right cervical lymph nodes. Her thyroid function tests were within normal limits. Ultrasonography of the neck revealed dominant solid hypoechoic nodule in right lobe of thyroid measuring 5.9 x 5.2 x 2.8 cm with internal vascularity and without any cystic changes. Computed tomography (CT) in the neck revealed heterogeneously enhancing lesion with areas of necrosis and calcification involving the right lobe and isthmus with ill-defined margins in places and mildly enlarged, necrotic level 3, 4 and 5 lymph nodes (Figure 1). Ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration cytology was suggestive for malignancy, possibly medullary carcinoma/poorly differentiated carcinoma (Bethesda category VI). Her serum calcitonin and urine catecholamines levels were within normal limits.
After detailed discussion and consent she underwent total thyroidectomy and bilateral neck node clearance. Intraoperative clinical findings of the tumour in right lobe of the thyroid showed desmoplastic reaction in surrounding soft tissues with no local invasion on the right side. The left lobe was apparently uninvolved and the postoperative course was uneventful.
Figure 1: Computed tomography of the neck showing a heterogeneously enhancing infiltrative mass in the right thyroid lobe and isthmus (large arrow) with enlarged lymph nodes (small arrow)

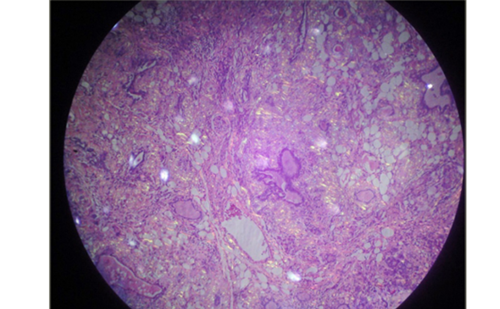
Figure 2: Histopathological examination showing sheets of tumour cells with oval to spindle nuclei and clumped chromatin

Figure 3: Immunohistochemistry showing strong membranous and cytoplasmic positivity of smooth muscle actin in tumour cells
Histopathology showed spindle cells with high-grade sarcoma of the thyroid origin, likely LMS (Figure 2). Eight out of 41 lymph nodes sent for biopsy were tumour positive. Immunohistochemistry showed that neoplastic spindle cells were positive for smooth muscle actin (Figure 3), vimentin, caldesmon and had Ki-67 index of 60%; while no reactivity was reported for thyroglobulin, calcitonin, thyroid transcription factor-1, S-100, CD45, CD 34, paired box gene-8 (PAX-8), chromogranin and cytokeratins.
A positron emission tomography scan conducted postoperatively and showed no evidence of residual tissue and distant metastasis. The patient was then planned for radiotherapy after stabilisation; however, within 1 month of the waiting period, she developed local recurrence. The oncology team were consulted and she received 35 cycles of radiotherapy and paclitaxel and carboplatin-based chemotherapy. During last follow-up telephonically 5 months post-surgery she was alive; however, in a very poor general condition.
Discussion
Primary LMS of the thyroid gland is a rare tumour. Among all tumours of the thyroid gland, primary thyroid LMS accounts only for 0.014%.17 They usually develop in older people (mean age 66 years) with no gender predisposition.20 Primary thyroid LMS most commonly presents as a painless, rapidly-growing neck mass. Onset of tumour, which usually develops in one lobe of the thyroid, is sudden and the tumour spreads rapidly to surrounding tissues as seen in our case.18 Additional symptoms may include hoarseness, dysphagia, dyspnoea and weight loss. The aetiology of these tumours is not very clear; however, they are thought to develop from the smooth muscles of the capsular veins in the thyroid gland.24 It is also suggested that primary thyroid LMS may develop as a result of smooth muscle metaplasia in a thyroid anaplastic carcinoma.25 Infection with Epstein-Barr virus is also suspected in a previous case report.6 In contrast to anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid, cervical metastasis is less common in LMS. Distant metastasis has been reported in lungs, lymph nodes, liver, myocardium, kidney, pancreas, small bowel, colon, peritoneum, brain, and bones.20
Histological features are typically the presence of interlacing fascicles or bundles of eosinophilic spindle cells with abundant acidophilic fibrillary cytoplasm and with a nucleus generally centrally located and typically blunt-ended or ‘cigar-shaped’. The degree of nuclear atypia, as well as the mitotic activity, varies considerably. Although high mitotic index is virtually diagnostic of malignancy, a primary thyroid LMS must be strongly suspected for a tumour that is widely necrotic, haemorrhagic and with significant atypia, even if the mitotic activity is low.15 On Immunohistochemistry, positivity for smooth muscle actin, vimentin, desmin and caldesmon may diagnose thyroid LMS, while these tumour cells don’t react to keratin, thyroglobulin, chromogranin, and calcitonin.8
Although there are various approaches for treatment, from aggressive surgery to adjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy, none of these have shown a positive effect on the high recurrence rate and poor survival of these tumours.16 A recent review of published cases indicated that 14 out of 23 patients died within months; four of the seven who survived had a recurrent and/or metastatic disease. Among these, the longest duration of the patient to be disease-free was 5 years.18
In conclusion, as primary LMS is a rare malignancy of the thyroid, it should be suspected in all patients presenting with rapidly growing mass at the anterior neck. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial, and immunohistochemistry is necessary to differentiate it from other aggressive malignancies of thyroid. LMS is an aggressive tumour with poor prognosis and without any established treatment.⬛