Search Results
Showing Results for metabolic dysregulation
Article highlights There is growing clinical importance attributed to the development of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D). Numerous international groups now advocate screening for advanced fibrosis in people with risk factors, such as ...
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrinopathy affecting women of reproductive age and is characterized by hyperandrogenism, anovulation and insulin resistance (IR).1 Women with PCOS have a high risk of developing type 2 diabetes (T2D), dyslipidaemia, hypertension and ...
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) is a ubiquitous, multifunctional, 766-amino acid, type 2 transmembrane glycoprotein, which participates in the regulation of metabolic functions, immune and inflammatory responses, cancer growth and cell adhesion.1 It has two forms: the first is a membrane-bound form, which ...

Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is generally defined as “any degree of glucose tolerance with onset or first recognition during pregnancy”.1 It currently is one of the diseases with the highest morbidity among pregnant women.2 Determining its prevalence has been a ...
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is a non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma originating from the germinal center, characterized by dysregulation of the MYC gene, often resulting from the translocation of chromosome 8 into 14. It is extremely aggressive, representing the fastest proliferating cancer, and typically involves ...

There has been an exponential increase in the global prevalence of obesity over the past few decades because of adverse lifestyle choices, such as physical inactivity and overconsumption of macronutrients. The obesity pandemic has contributed to more than 50 different disorders ...

Article highlights Epigenetics refers to the heritable changes in DNA expression without changes in the genetic code. Epigenetic changes are brought about by post-translational modifications of histone proteins, covalent modifications of DNA bases and microRNA. Epigenetics explains how environmental milieu ...

In the early 1970s, the discovery of statin by Dr Akira Endo changed the fate of cardiovascular disease prevention and the treatment of atherosclerosis. It was during this period that the rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis was revealed, and the ...

For people with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) or type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), glycaemic control has been monitored by two key measurements: laboratory-tested glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) level and the individuals’ self-monitored blood glucose (SMBG) fingerprick testing.1,2 Both of ...

Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycaemia resulting from insulin resistance, inefficient insulin secretion and disproportionate glucagon secretion.1 It has been reported to be an expanding global health issue of the 21st century, and one of ...

Management of patients with severe COVID-19 remains a challenge for physicians. In severe cases of COVID-19, a hyperactive innate immune response characterized by high serum levels of proinflammatory markers, known as a ‘cytokine storm’, is characteristically present. The cytokine storm ...

According to the estimates of the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), one in every 11 adults of the global population has diabetes, with an overall disease prevalence of 425 million.1 This diabetes prevalence is expected to increase exponentially with time because of the ...

In a series of recent studies, insulin-stimulated glucose disposal in animal models and human subjects was found to be inversely related to plasma membrane cholesterol content. Aberrantly increased plasma membrane cholesterol is seen uniformly in insulin-resistant mice, rats, swine, and ...

From glucose homeostasis to hyperglycemia Glucose homeostasis is maintained by a complex neurohormonal system, which modulates peripheral glucose uptake, hepatic glucose production, and exogenous glucose utilization following food ingestion.1,2 This allows the maintenance of plasma glucose concentrations within normal range, ...

Moyamoya is a rare idiopathic cerebral vasculopathy characterized by stenosis of the terminal portion of the internal carotid arteries (ICAs) and the development of a thin collateral network of small vessels (“puff of smoke”), initially described as a primary disease ...
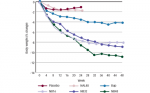
The growing prevalence of obesity is a global health concern. In 2009 to 2010, more than one-third of adults and 17 % of youth in the US were obese, as defined by body mass index (BMI). Obesity is associated with numerous health risks such ...

The growing prevalence of obesity is a global health concern. In 2009 to 2010, more than one-third of adults and 17 % of youth in the US were obese, as defined by body mass index (BMI). Obesity is associated with numerous health risks such ...

As a result of advanced medication regimens, particularly protease inhibitors (PIs), the life expectancy of HIV-infected adults has risen considerably. As a result of advanced medication regimens, particularly protease inhibitors (PIs), the life expectancy of HIV-infected adults has risen considerably. ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.

